Creating and Running a Docker Development Environment
by John Vincent
Posted on May 26, 2021
Build Docker images and run in Docker containers for a Development Environment.
This is part of a series of discussions regarding Deploying TaskMuncher, a React and Node application, to a Multi-Container Docker Environment at AWS using Dockerhub and Travis CI
For more details, please see Overview of Create Multi-Container Docker TaskMuncher Application at AWS
The following sections include
Overview
Docker images need to be built for
- Development
- Running the Production Application in a Development Environment
- Deployment to AWS production
To better understand this document, a review of the following is suggested
Development
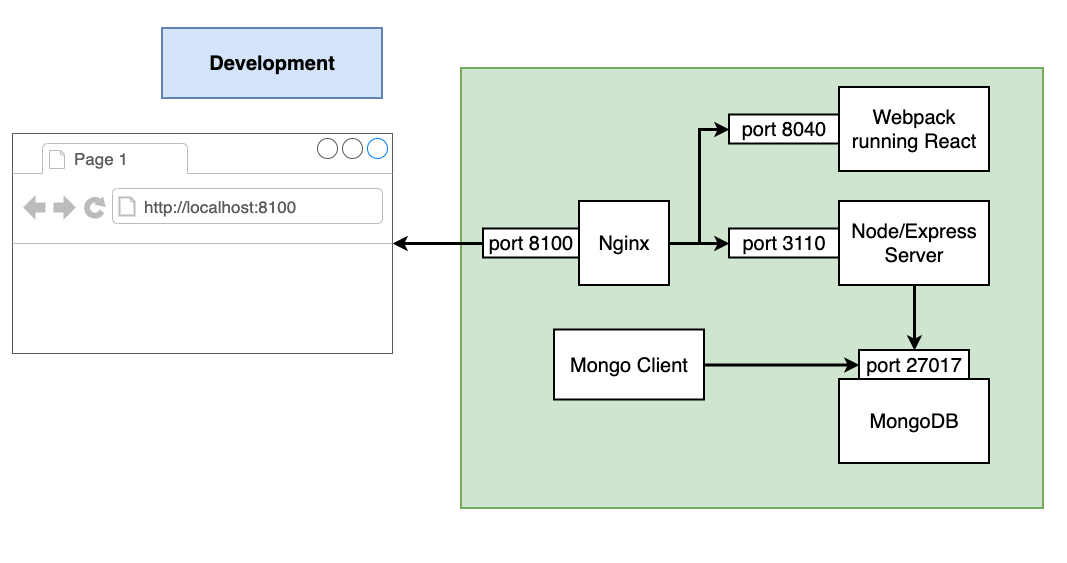
The Docker Development environment is required to
-
TaskMuncher Development.
-
Allow for the building and unit testing of a development system as part of the Travis-CI deployment to the AWS production environment.
Please review Configuring Makefiles to build and run Docker Images using Docker, Docker Compose and Dockerfile
Review make/dev.mk at Makefile for the Development Environment.
Notice targets
-dev-build- build the Docker image-dev-sh- starts the image in ashshell-dev-run- execute the Docker image in a Docker container
It is recommended to
-
dev-shinto an image to verify the file systems are as expected as it is very easy to incorrectly configure the image. -
-dev-runthe image in a container to verify it is running as expected. It is very easy to incorrectly configure the application.
Run make client-dev-jest and make server-dev-jest to test all unit tests.
Run client with make client-dev-run and test with
http://localhost:8040/
Client will run but not be able to connect to other services as they are not running.
Run server with make server-dev-run and access any public end points. The server will fail as cannot connect to MongoDB container.
To build all Docker images
make all-build
To remove all Docker images and containers
make all-clean
Running Development
The application is configured to use Docker Compose. Please review Makefile using Docker Compose for a Development Environment.
To start the application
make compose-dev-up
To run the application
localhost:8100
To stop the application
make compose-dev-down
Unit Testing for Travis-CI deployment
Please review Configure Travis-CI for Docker Multi-container Deployment to AWS
Notice in .travis.yml
before_install:
- docker build -t johnvincentio/taskmuncher-client -f ./config/client/dev/Dockerfile .
- docker build -t johnvincentio/taskmuncher-server -f ./config/server/dev/Dockerfile .
script:
- docker run -e CI=true johnvincentio/taskmuncher-client npm run test -- --coverage
- docker run -e CI=true johnvincentio/taskmuncher-server npm run test -- --coverage
which
- builds development version of
clientandserver - runs unit test on
clientandserver
Review make/dev.mk at Makefile for the Development Environment
Notice targets
client-dev-buildclient-dev-jestserver-dev-buildserver-dev-jest
which perform these tasks.
Review the Makefile at Makefile. Notice the target all-unit-tests
Thus, to run all unit tests
make all-unit-tests
Always ensure all unit tests are passing before attempting a deployment to production.
Production in Development Docker Containers
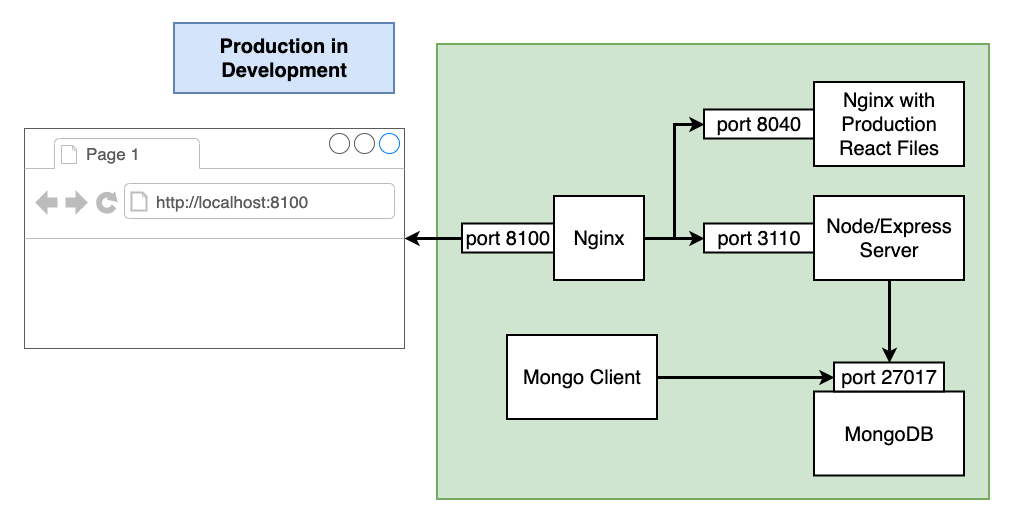
This application is configured to use Docker Compose. Please review Makefile using Docker Compose for a Development Environment.
To start the application
make compose-devprod-up
To run the application
localhost:8100
To stop the application
make compose-dev-down
AWS Production Docker Containers
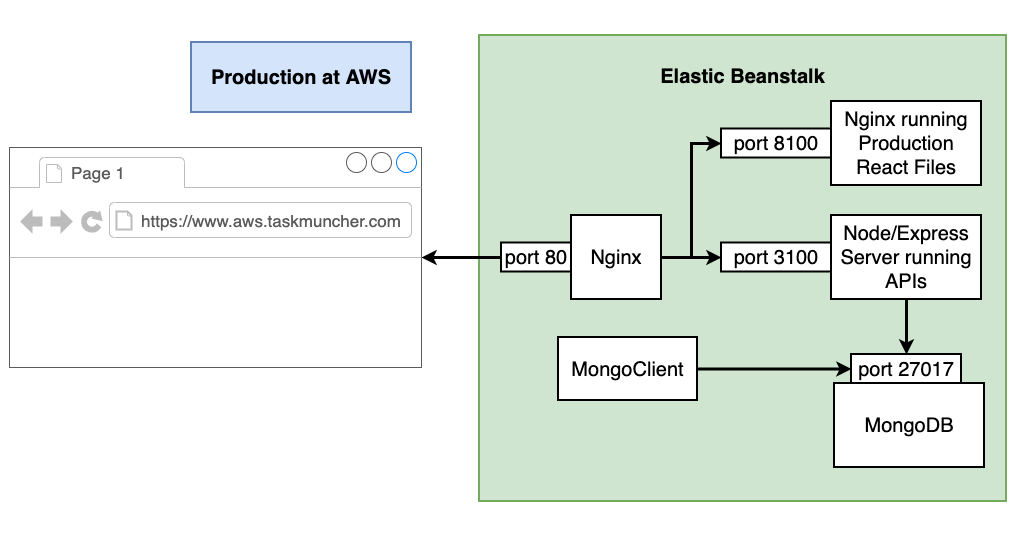
The Docker containers that are deployed to AWS production are created by Docker during the Travis-CI deployment. For details, see
-
Configuring Makefiles to build and run Docker Images using Docker, Docker Compose and Dockerfile
-
Configure Travis-CI for Docker Multi-container Deployment to AWS
Docker Logs
Docker can show Container logs
Docker Compose
Start the application using Docker Compose
make compose-dev-up
and check containers
docker ps -all
only shows the one container taskmuncher-dev_nginx_1
02130c9dc587 taskmuncher-nginx-dev "/docker-entrypoint.…" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8100->8100/tcp, :::8100->8100/tcp taskmuncher-dev_nginx_1
Showing the logs
docker logs taskmuncher-dev_nginx_1
reveals limited information.
Checking the Docker Desktop Application, it shows an application taskmuncher-dev running containers
taskmuncher-dev_nginx_1taskmuncher-dev_client_1taskmuncher-dev_api_1taskmuncher-dev_mongodb_1taskmuncher-dev_mongo-client_1which has exited(0)
To show detailed logs of the other containers
docker logs taskmuncher-dev_client_1
docker logs taskmuncher-dev_api_1
docker logs taskmuncher-dev_mongodb_1
docker logs taskmuncher-dev_mongo-client_1
Stop the application
make compose-dev-down
Docker
Start a Docker container using Docker
make client-dev-run
and check containers
docker ps -all
only shows the one container taskmuncher-client-dev
e4ce00694599 taskmuncher-client-dev-image:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" 8 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:3110->3110/tcp, :::3110->3110/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8040->8040/tcp, :::8040->8040/tcp taskmuncher-client-dev
Showing the logs
docker logs taskmuncher-client-dev
reveals detailed logs.
MongoDB
For Local MongoDB, see Installing Mac MongoDB
Start Local MongoDB
./start-database
To show MongoDB version
cd mongodb/bin
mongo --version
Connect to local MongoDB
I recommend Robo 3T MongoDB GUI Client Application.
To access Local MongoDB with Robo 3T, set Connection parameters as follows
- Type: Direct Connection
- Name: MongoDB on Mac local
- Address: localhost
- Port: 27017
Robo 3T will connect to the local instance of MongoDB.
MongoDB in a Docker Container
Let's start by running a Development version
make compose-dev-up
Notice that this starts the whole application, including a MongoDB database that is seeded with initial data.
To verify this is the correct set of data, start the application and add a new goal.
localhost:8100
To view the MongoDB data
To access the MongoDB running in the Docker Containers with Robo 3T, set Connection parameters as follows
- Type: Direct Connection
- Name: MongoDB on Docker Container
- Address: localhost
- Port: 27017
Robo 3T will connect to the local instance of MongoDB.
Notice the database has been added correctly, look for the new data in Collections.
Stop the containers
make compose-dev-down
Network Tools
Configuring Docker containers can be a balancing act between the desire for useful features and the desire for a small image for better performance.
Network configuration problems can be especially hard to diagnose.
It can sometimes be helpful to install netstat.
To better understand this document, a review of the following is suggested
Adding Network Tools to MongoDB Image
The MongoDB image is based on Ubuntu 20.04. Install net-tools
Edit ./config/mongodb/Dockerfile
...
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y nginx curl gnupg2 wget net-tools
...
and build the image
make mongodb-dev-build
then run the image in a Docker container in one terminal
make mongodb-dev-run
and in another terminal, connect to the container
make mongodb-dev-connect
and run
netstat -a
returning
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:27017 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 2e135aa931ff:27017 172.17.0.1:58130 ESTABLISHED
Active UNIX domain sockets (servers and established)
Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path
unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 527867 /tmp/mongodb-27017.sock
which is helpful.
It should be noted that the following will also work.
docker exec taskmuncher-mongodb-dev netstat -a