Migration of johnvincent.io to Next.js from Gatsby
by John Vincent
Posted on January 17, 2021
A discussion of the practical steps I took to perform a migration from Gatsby to Next.js
Migration to Next.js from Gatsby
As this is a migration I would prefer to make the fewest changes possible. The architecture I have employed may not be optimal for Next.js but it is a practical solution.
I used Next.js to build statically generated pages, which is the same as Gatsby. These pages are served by a Nginx server.
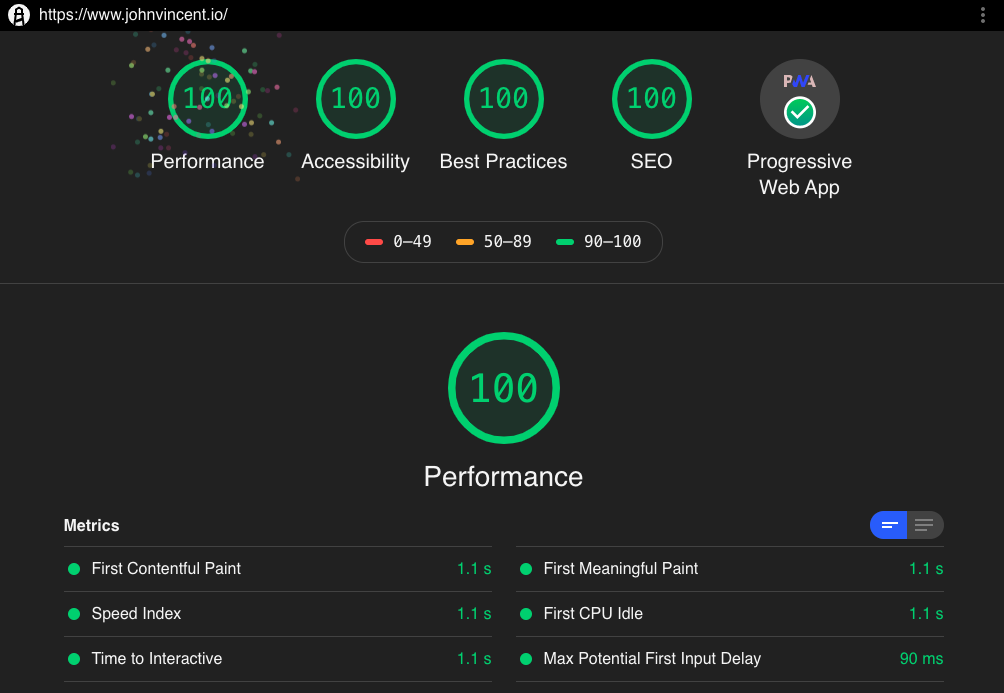
Gatsby Lighthouse Scores
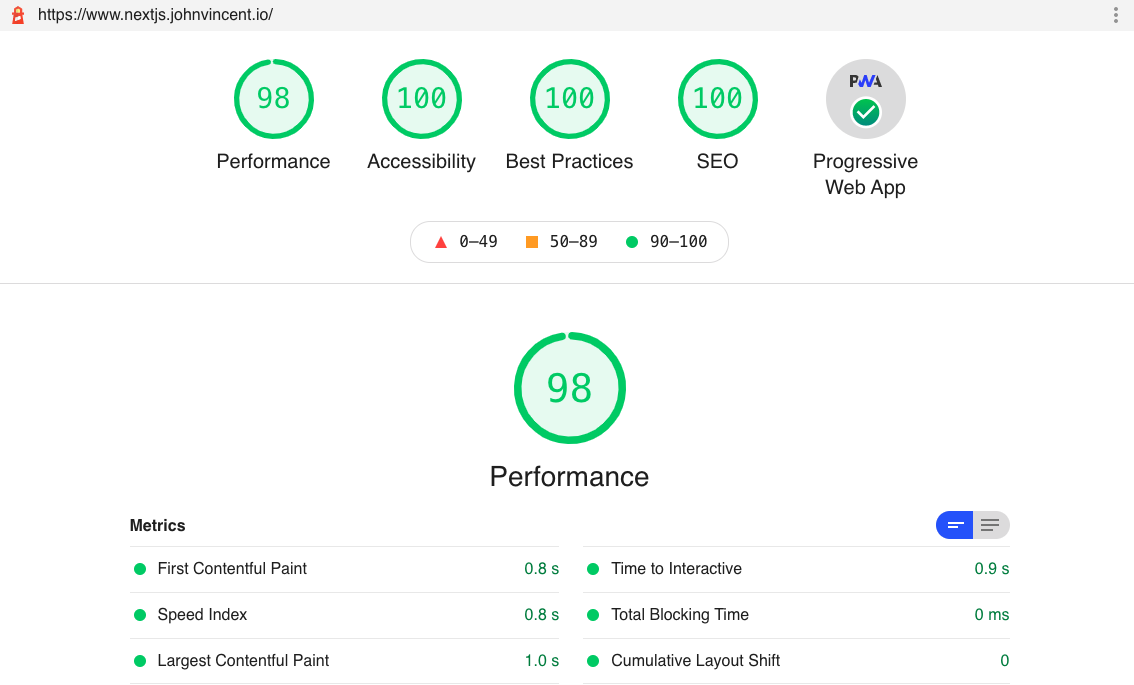
Next.js Lighthouse Scores
package.json
- Removed Gatsby packages.
- Added
next,next-pwa,gray-matter,globby - Changed
scriptsto:
"scripts": {
"dev": "JV_MODE=development next -p 3200",
"dev:prod:build": "JV_MODE=local_production next build",
"dev:prod:start": "JV_MODE=local_production next start -p 3225",
"production": "JV_MODE=production next build && JV_MODE=production next export"
}
This allows for:
- development mode
- production mode in a development environment
- production mode in a production environment
.gitignore
For Gatsby
.cache/
public
For Next.js
.next
out
public/feed.xml
public/sitemap.xml
public/sw.js
public/sw.js.map
public/workbox-*
The public files are excluded as they will generated by the build.
Visual Studio Code Debugger
Add to .vscode/launch.json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "node",
"request": "attach",
"name": "ORIG",
"skipFiles": ["<node_internals>/**"],
"port": 9229
}
]
}
To run the debugger
- Set a break point
- Select Debug mode
- Select
node.js (preview) - Select
Run Script: dev nextjs-website - Start the debugger
- Run the app
http://localhost:3200/
Debugger will stop at the break point.
Static files
Gatsby uses static. For Next.js, rename to public
Gatsby uses public for generated files.
Favicons
Gatsby uses a plugin gatsby-plugin-manifest
For Next.js, I built a component SEO to handle <head>
import React from 'react';
import Head from 'next/head';
import { seoType } from '../types';
const SEO = ({ seo }) => (
<Head>
<title>{seo.title}</title>
<meta charSet="utf-8" />
<meta httpEquiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1,shrink-to-fit=no" />
<meta name="google-site-verification" content={seo.googleSiteVerification} />
<meta name="description" content={seo.description} />
<meta name="keywords" content={seo.keywords} />
<meta name="author" content={seo.author} />
<meta name="image" content={seo.image} />
<script type="application/ld+json">{JSON.stringify(seo.schemaOrgJSONLD)}</script>
<meta property="fb:app_id" content={seo.fbAppId} />
{/* OpenGraph */}
<meta property="og:locale" content={seo.locale} />
<meta property="og:type" content={seo.type} />
<meta property="og:title" content={seo.title} />
<meta property="og:description" content={seo.description} />
<meta property="og:url" content={seo.url} />
<meta property="og:image" content={seo.image} />
<meta property="og:image:width" content="449" />
<meta property="og:image:height" content="449" />
{/* Twitter Card */}
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary" />
<meta name="twitter:title" content={seo.title} />
<meta name="twitter:description" content={seo.description} />
<meta name="twitter:site" content={seo.twitterCreator} />
<meta name="twitter:image" content={seo.image} />
<meta name="twitter:creator" content={seo.twitterCreator} />
<link rel="icon" type="image/png" sizes="32x32" href="/icons/favicon-32x32.png" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/png" sizes="16x16" href="/icons/favicon-16x16.png" />
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="/icons/icon-48x48.png" />
<link rel="manifest" href="/manifest.webmanifest" />
<meta name="msapplication-TileColor" content="#da532c" />
<meta name="theme-color" content="#ffffff" />
<link rel="mask-icon" href="/icons/safari-pinned-tab.svg" color="#5bbad5" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="48x48" href="/icons/icon-48x48.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="72x72" href="/icons/icon-72x72.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="96x96" href="/icons/icon-96x96.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="144x144" href="/icons/icon-144x144.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="180x180" href="/icons/icon-180x180.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="192x192" href="/icons/icon-192x192.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="256x256" href="/icons/icon-256x256.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="384x384" href="/icons/icon-384x384.png" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" sizes="512x512" href="/icons/icon-512x512.png" />
<link rel="canonical" href={seo.canonicalUrl} />
<link rel="alternate" type="application/rss+xml" title="John Vincent Blog Feed" href={seo.seoFeed} />
<link rel="sitemap" type="application/xml" href="/sitemap.xml" />
<base href={seo.baseUrl} />
</Head>
);
SEO.propTypes = {
seo: seoType.isRequired,
};
export default SEO;
This allows for different content for different Pages.
Use canonical tag
I am keeping both Gatsby and Next.js websites, so I use:
<link rel="canonical" href={seo.canonicalUrl} />
which references the same page in the Gatsby site johnvincent.io
PWA
PWA in Next.js is implemented with the package next-pwa
next.config.js
For Next.js, use next.config.js
const withPWA = require('next-pwa');
const runtimeCaching = require('next-pwa/cache');
module.exports = withPWA({
trailingSlash: true,
pwa: {
dest: 'public',
disable: process.env.JV_MODE !== 'production',
runtimeCaching,
publicExcludes: []
},
env: {
JV_MODE: process.env.JV_MODE
},
webpack: (config, { isServer }) => {
if (isServer) {
require('./src/scripts/sitemap');
require('./src/scripts/rss');
}
return config;
}
})
Note:
JV_MODEis set inpackage.jsonrequire('./src/scripts/sitemap')will create thesitemap.xmlrequire('./src/scripts/rss')will create theRSS Feed- Package
next-pwais used to make a PWA.- PWA is only enabled for Production.
Generated files conventions
Gatsby generates file/index.html
Next.js generates file.html
Next.js can be configured to behave the same as Gatsby with a change to next.config.js
trailingSlash: true
Sitemap
Gatsby uses a plugin gatsby-plugin-sitemap
For Next.js, I created src/scripts/sitemap.js
const globby = require("globby");
const prettier = require("prettier");
const libs = require("./libs");
const getDate = new Date().toISOString();
const MY_DOMAIN = "https://nextjs.johnvincent.io";
const formatted = sitemap => prettier.format(sitemap, { parser: "html" });
(async () => {
const pages = await globby([
// include
"src/pages/**/*.jsx",
// exclude
"!src/pages/_app.jsx",
"!src/pages/\\[...slug\\].jsx",
"!src/pages/404.jsx",
"!src/pages/thanks.jsx"
]);
const posts = libs.createPosts().sort((a, b) => (a.frontmatter.permalink > b.frontmatter.permalink) ? 1 : -1);
const pagesSitemap = `
${pages
.map(page => {
const pathname = page
.replace("src/pages/", "")
.replace(".jsx", "")
.replace(/\/index/g, "");
const routePath = pathname === "index" ? "" : pathname;
return `<url>
<loc>${MY_DOMAIN}/${routePath}</loc>
<lastmod>${getDate}</lastmod>
</url>`;
})
.join("")}
`;
const postsSitemap = `
${posts
.map(post => {
return `<url>
<loc>${MY_DOMAIN}${post.frontmatter.permalink}</loc>
<lastmod>${new Date(post.mtime).toISOString()}</lastmod>
</url>`;
})
.join("")}
`;
const generatedSitemap = `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset
xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9 http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9/sitemap.xsd"
>
${pagesSitemap}
${postsSitemap}
</urlset>`;
const formattedSitemap = [formatted(generatedSitemap)];
libs.writeSitemap(formattedSitemap);
})();
RSS Feed
Gatsby uses a plugin gatsby-plugin-feed
For Next.js, I created src/scripts/rss.js
const libs = require("./libs");
const MY_DOMAIN = "https://www.nextjs.johnvincent.io";
(async () => {
const posts = libs.createPosts().sort((a, b) => (a.modifiedTime > b.modifiedTime) ? -1 : 1);
const postsFeed = `
${posts
.map(post => {
const categories = post.frontmatter.category.map(cat => {
return `<category>${cat}</category>\n`;
}).join("");
return `<item>
<title><![CDATA[${post.frontmatter.title}]]></title>
<link>${MY_DOMAIN}${post.frontmatter.permalink}</link>
<description><![CDATA[${post.excerpt}]]></description>
<pubDate>${post.postDate}</pubDate>
<guid isPermaLink="true">${MY_DOMAIN}${post.frontmatter.permalink}</guid>
${categories}
</item>
`;
})
.join("")}
`;
const generatedFeed = `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rss
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
xmlns:content="http://purl.org/rss/1.0/modules/content/"
xmlns:atom="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom"
version="2.0"
>
<channel>
<title><![CDATA[John Vincent Blog Feed]]></title>
<description><![CDATA[John Vincent Blog Feed]]></description>
<link>${MY_DOMAIN}</link>
<lastBuildDate>${new Date().toUTCString()}</lastBuildDate>
<atom:link href="${MY_DOMAIN}/feed.xml" rel="self" type="application/rss+xml"/>
<generator>John Vincent Generator</generator>
<managingEditor>other@johnvincent.io (John Vincent)</managingEditor>
<webMaster>other@johnvincent.io (John Vincent)</webMaster>
${postsFeed}
</channel>
</rss>
`;
libs.writeRssFeed(generatedFeed);
})();
To validate the generated RSS Feed use a Feed Validation Service
robots.txt
Gatsby uses plugin gatsby-plugin-robots-txt
For Next.js, I built /public/robots.txt
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://www.nextjs.johnvincent.io/sitemap.xml
Host: https://www.nextjs.johnvincent.io
Sass
Gatsby uses plugin gatsby-plugin-sass and gatsby-browser.js
/**
* Implement Gatsby's Browser APIs in this file.
*
* See: https://www.gatsbyjs.org/docs/browser-apis/
*/
import './src/styles/styles.scss';
For Next.js, pages/_app.jsx
import '../styles/styles.scss';
function MyApp({ Component, pageProps }) {
return <Component {...pageProps} />
}
export default MyApp;
Page Generation
Gatsby uses gatsby-node.js and makes extensive use of GraphQL
For Next.js, the approach is very different.
Next.js Pages
The general form of a pages Component is:
import React from 'react';
import MainLayout from '../components/MainLayout';
import Intro from '../components/Intro';
import Services from '../components/Services';
import CallToAction from '../components/CallToAction';
import createMetaData from '../lib/createMetaData';
import json from '../data/pages/home.json';
const Home = () => {
// console.log('Home; page ', json);
const { site, page, seo } = createMetaData(json);
return (
<MainLayout site={site} page={page} seo={seo}>
<Intro page={page} />
<Services />
<CallToAction />
</MainLayout>
);
};
export default Home;
Notice import json from '../data/pages/home.json' which directly imports the content for the page. As the content is static, this architecture is sufficient.
Dynamic Urls
Next.js, by convention, will treat all .js and .jsx files in src/pages as pages that need to be generated. Further, Next.js generates pages with Urls that match the pages folder structure and files within that structure.
However, the Markdown files do not follow these rules and instead have some specific rules.
- The published date of the file is in the filename.
For example
2020-11-17-nextjs-migration.md - The url of the page is in the
FrontMatterof theMarkdownfile.
Thus the architectural requirement to use pages/[...slug].jsx to build all other pages.
[...slug].jsx
import React from 'react';
import BlogPostTemplate from '../templates/BlogPostTemplate';
import ContentTemplate from '../templates/ContentTemplate';
import BlogTemplate from '../templates/BlogTemplate';
import getAll from '../lib/posts';
import capitalize from '../lib/utils';
export default function Page({ page, pageData, type }) {
if (!page) {
return null;
}
if (type === 'blogPost') return (
<BlogPostTemplate data={page.node} pageData={pageData} />
);
if (type === 'content') return (
<ContentTemplate data={page.node} />
);
if (type === 'blogPage') return (
<BlogTemplate pageData={pageData} />
)
return null;
}
export async function getStaticPaths() {
const { posts, content, blogPageData } = getAll();
const postPaths = posts.map(post => {
const slug = post.node.fields.permalink.split('/').slice(1);
return { params: { slug } };
});
const contentPaths = content.map(post => {
const slug = post.node.fields.permalink.split('/').slice(1);
return { params: { slug } };
});
const blogPagePaths = blogPageData.pageData.map(item => {
const slug = item.path.split('/').slice(1);
return { params: { slug } };
})
return {
paths: [ ...postPaths, ...contentPaths, ...blogPagePaths],
fallback: false
}
}
export async function getStaticProps({ params }) {
const { posts, content, blogPageData, categories } = getAll();
const currentPath = `/${params.slug.join('/')}/`;
const idx1 = posts.findIndex(item => item.node.fields.permalink === currentPath);
if (idx1 > -1) {
const page = posts[idx1];
const prevNode = idx1 === 0 ? null : posts[idx1 - 1].node;
const nextNode = idx1 === posts.length - 1 ? null : posts[idx1 + 1].node;
const pageCategories = {};
page.node.frontmatter.category
.sort((a, b) => a.toLowerCase().localeCompare(b.toLowerCase()))
.forEach((arrayItem) => {
const category = capitalize(arrayItem.toLowerCase());
const value = categories[category];
pageCategories[category] = value;
});
return { props:
{ page, type: 'blogPost', pageData: { prevNode, nextNode, categories: pageCategories } }
};
}
const idx2 = content.findIndex(item => item.node.fields.permalink === currentPath);
if (idx2 > -1) {
return { props: { page: content[idx2], type: 'content' } };
}
const idx3 = blogPageData.pageData.findIndex(item => item.path === currentPath);
if (idx3 > -1) {
const blogPage = blogPageData.pageData[idx3];
const pagePosts = posts.slice(blogPage.from, blogPage.to);
const { pagesTotal } = blogPageData;
const { currentPage } = blogPage;
return { props:
{ page: {},
type: 'blogPage',
pageData: {
posts: pagePosts,
categories,
page: { currentPage, pagesTotal }
}
}
};
}
return { props: { page: { notfound: true }, type: '' } };
}
where lib/posts.js
import fs from 'fs';
import matter from 'gray-matter';
import { splitter, formatDate, calculateCategories } from './utils';
const POSTS_PER_PAGE = 69;
const STATIC_POSTS = createPosts();
const STATIC_CONTENT = createContent();
const STATIC_CATEGORIES = calculateCategories(STATIC_POSTS);
const STATIC_BLOG_PAGES = createBlogPages(STATIC_POSTS);
export default function getAll() {
return {
posts: STATIC_POSTS,
content: STATIC_CONTENT,
categories: STATIC_CATEGORIES,
blogPageData: STATIC_BLOG_PAGES
}
}
function createBlogPages(posts) {
const totalBlogs = posts.length;
const postsPerPage = POSTS_PER_PAGE;
const pagesTotal = Math.ceil(totalBlogs / postsPerPage);
// console.log('pagesTotal ', pagesTotal);
const pageData = [];
for (let i = 1; i <= pagesTotal; i++) {
const from = (i - 1) * postsPerPage;
const to = i * postsPerPage;
// console.log('from ', from, ' to ', to);
const path = i === 1 ? '/blog/' : `/blog/page${i}/`;
pageData.push({
path,
from,
to,
currentPage: i,
});
}
return {
totalBlogs,
postsPerPage,
pagesTotal,
pageData
}
}
function createPosts() {
// console.log('createPosts');
const results = walk(`${process.cwd()}/src/markdown/blogs`);
const posts = results.map(({ path, name }, index) => {
// console.log('path ', path);
const markdownWithMetadata = fs.readFileSync(`${path}`).toString();
// console.log('markdownWithMetadata ', markdownWithMetadata);
const { content, data, excerpt } = matter(markdownWithMetadata, { excerpt: handleExcerpt });
const [, dateString, title] = splitter(name);
const modifiedTime = new Date(`${dateString} 14:30:00`).getTime();
const postDate = formatDate(new Date(`${dateString} 14:30:00`));
// console.log('data ', data);
return {
node: {
id: `key_${index+1}`,
html: content,
frontmatter: data,
excerpt,
fields: {
modifiedTime,
permalink: data.permalink,
postDate,
slug: data.permalink,
suburl: title.trim(),
type: 'blog'
}
}
};
});
// console.log('**** posts ', posts);
return posts.sort(compare);
}
function createContent() {
// console.log('createContent');
const results = walk(`${process.cwd()}/src/markdown/content`);
const posts = results.map(({ path, name, mtime }, index) => {
// console.log('path ', path);
const markdownWithMetadata = fs.readFileSync(`${path}`).toString();
// console.log('markdownWithMetadata ', markdownWithMetadata);
const { content, data } = matter(markdownWithMetadata);
const postDate = formatDate(new Date(mtime));
// console.log('postDate ', postDate);
return {
node: {
// id: index + 1,
html: content,
frontmatter: data,
fields: {
modifiedTime: mtime,
permalink: data.permalink,
postDate,
slug: data.permalink,
suburl: name.trim()
}
}
};
});
return posts;
}
function compare(a, b) {
if (a.node.fields.modifiedTime < b.node.fields.modifiedTime) return 1;
if (a.node.fields.modifiedTime > b.node.fields.modifiedTime) return -1;
return 0;
}
function handleExcerpt(file, options) {
const list = [];
const lines = file.content.split('\n').slice(0, 20);
let add = true;
lines.every(line => {
// console.log('line :',line,':');
if (line === '<!-- end -->') add = false;
if (add) list.push(line);
return add;
})
file.excerpt = list.join('\n');
}
function walk(dir) {
let results = [];
const list = fs.readdirSync(dir);
list.forEach(file => {
// console.log('file ', file);
if (file !== ".DS_Store") {
// const [, dateString, title] = splitter(file);
// console.log('dateString ', dateString);
// console.log('title ', title);
const path = `${dir }/${ file}`;
const stat = fs.statSync(path);
if (stat && stat.isDirectory()) {
results = results.concat(walk(path));
} else {
const mtime = (new Date(stat.mtime).getTime());
results.push({
file,
path,
name: file.slice(0, -3),
mtime
});
}
}
});
return results;
}
Code changes for Next.js
The following are some general changes
Link tag
Gatsby
import { Link } from 'gatsby';
<Link to={item.href}>{item.text}</Link>
Next.js
import Link from 'next/link';
<Link href={item.href}><a>{item.text}</a></Link>
Notice the additional requirement of an anchor tag.
head tag
Gatsby uses react-helmet
<Helmet title={seo.title}>
Next.js uses import Head from 'next/head'
<Head>
<title>{seo.title}</title>
Rendering Markdown
Gatsby
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: html }} />
Next.js, use package react-markdown
import ReactMarkdown from 'react-markdown/with-html';
<div>
<ReactMarkdown escapeHtml={false} source={html} />
</div>
Development
Next.js uses folder .next
"scripts": {
"dev": "JV_MODE=development next -p 3200"
}
Build
npm run dev
To test the app localhost:3200
Production in Development
Always build and thoroughly test a production ready system in development before pushing to production.
"scripts": {
"dev:prod:build": "JV_MODE=local_production next build",
"dev:prod:start": "JV_MODE=local_production next start -p 3225"
}
Build
npm run build
npm run start
To test the app localhost:3225
Production
"scripts": {
"production": "JV_MODE=production next build && JV_MODE=production next export"
}
Build
npm run production
which creates folder /out
Deploy to Production
For details, see Overview of port to Next.js from Gatsby